Degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the spine are a form of a person that pays the price of walking straight. It is known that other mammals do not experience bone necrosis, since their spine is horizontal to the surface of the earth. The vertical load during walking leads to a gradual destruction of the cartilage tissue of the disc and contributes to displacement of the vertebrae into a dangerous location.

In the thoracic region, such processes occur less frequently in the sacrum and cervix, but this does not reduce the severity of the disease. This article will cover symptom issues and treatment of thoracic necrosis in detail, as well as items related to the prevention of the disease.
Characteristics of thoracic necrosis
The thoracic spine is characterized by low mobility, which reduces the likelihood of degeneration in this area. However, cases of this disease are frequently reported by orthopedic and trauma doctors in different age groups.
In recent decades, the incidence of osteonecrosis in civilized countries has steadily increased. Doctors believe that the main reasons for this trend are inactive lifestyles, poor diets, and common environmental background on the planet.
Women experience necrosis of the rib cage, 2-3 times more often than men. This is due to the specifics of the female anatomy and physiology. Other influencing factors are: childbirth, heel walking, general weakness of the ligamentous muscle in women.
In both sexes, thoracic necrosis causes painful symptoms and decreased range of motion. The progression of the pathology is accompanied by compression of nerve ends, which inevitably affects the state of internal organs. Severe cases of the disease are often accompanied by dysfunction of the blood vessels and the heart, problems with breathing.
Anatomically, the 12 thoracic vertebrae are connected to the ribs and sternum to form a sturdy and inactive frame structure to protect the internal organs from mechanical stress. In the early stages, the disease almost does not cause severe symptoms, but in the later stages, the manifestations of the pathology are so diverse that sometimes this interferes with an accurate diagnosis. No wonder bone necrosis is commonly known as "chameleon disease".The most common causes of breast cancer are trauma, muscle weakness, inactivity, metabolic disorders, high back stress, genetics. The disease develops gradually, on the one hand it enables the patient to initiate treatment in time and prevents the degenerative process, but on the other hand, it prevents early detection of the disease.
Stages
Doctors classify thoracic tumors according to the stages of their development:
Stage 1.The disc has lost elasticity, decreased in size, but has not yet moved from the anatomic position.
Stage 2.The height of the disc decreases further and the spine itself loses stability. Cracks form in the spacer, the discs shift and put pressure on nerve, blood vessel, and muscle ends. The second stage is characterized by severe back pain and neurological symptoms.
Stage 3.Degradation can lead to the development of protrusions and rupture of the annular filament. In such cases, a herniated disc is diagnosed. Discs lose their cushioning properties and no longer perform their proper anatomical functions. The vertebrae themselves are also affected - they join together, collapse and form bones - dangerous bone growth.
In addition to hard tissue, muscles, ligaments and tendons are also affected. Muscle is tightened, spasm occurs in it. The body tries to fix the affected area as much as possible to relieve pain - this leads to muscle congestion and muscle atrophy.
Symptoms of bone necrosis of the chest
As mentioned, at the onset stage, thoracic necrosis is either weak or completely absent. As the pathology progresses, periodic attacks occur between the shoulder blades: symptoms increase after physical activity or vice versa, after prolonged rest. Usually, the pain disturbs the patient in the morning after waking up and fades within an hour. Sometimes the pain travels along the intercostal nerve, spreading to the chest when coughing, sneezing, running.
Featured markers
At stage 2-3, the most obvious symptom of thoracic necrosis is constant pain in the interstitial region. Chest pain is also quite typical: it feels like the angina caused by coronary artery disease or heart failure.
Similarity of symptoms to heart disease is a fairly common cause of misdiagnosis. However, it is quite simple to distinguish pain during degenerative spine from heart symptoms: nitroglycerin and similar drugs reduce angina, with osteonecrosis, do not relieve the condition. of the patient in any way.
Other characteristic symptoms of thoracic tumor:
- Tens up the muscles of the body during deep breathing (back pain) - as if the body were being squeezed with a ring;
- Low back pain - a throbbing pain in the chest (the so-called "low back pain in the chest");
- A sensation of goosebumps and numbness in the hand (when lens syndrome is present);
- Intercostal pain during walking and physical activity (intercostal pain): with inflammation of the nerve end, pain becomes intermittent;
- Lumbar cramps;
- Pain when raising hands, rotating trunk and taking deep breaths.
The stages of the disease directly affect the intensity of symptoms. For the patient in the treatment plan, it is important not to get rid of the pain with medications and unique methods (pain relievers, antispasmodics, ointments, compresses and heating pads)but should go to the clinic and find out the cause of the pain from the doctor. Self-treatment of osteonecrosis is rarely effective and, in some cases, even aggravates the course of the disease.
Rare symptoms
Chest bone tumors are often disguised as other pathologies, causing their symptoms. This complicates the diagnosis and is often the cause of inadequate treatment.
Atypical manifestations of the disease are diverse:
- Signs of ischemia, heart attack, myocardial infarction (electrocardiogram or other tests should be performed to make differential diagnosis);
- Pain associated with breast diseases in women: to rule out the presence of a tumor, you should be examined by a breast specialist;
- Wounds like gastritis, colitis, stomach or intestinal ulcers, hepatitis - to rule out these diseases, a gastroenterologist will prescribe the diagnosis;
- Paroxysmal abdominal pain corresponding to pain in the kidneys or other diseases of the urinary system.
Urinary disorders and reproductive system disorders are also possible. Women suffer from heavy menstrual bleeding, painful and heavy periods (menorrhagia), and sometimes infertility. Men with erectile dysfunction. Doctors do not always find the true cause of these pathologies, and therefore the treatment of reproductive diseases does not have a positive effect.
Occasional bone necrosis in chest area, increased pressure, toothache and headache, sleep disturbance, tinnitus. Psychological disturbances are not excluded - irritability, depression, tearfulness, anxiety.
Diagnosis, treatment and prevention
Examination of the appearance, palpation, and multiple movements are performed to detect disease. It is important to learn in detail from the patient the timing of the symptoms, their nature and the concomitant manifestations of the disease.
The following procedures are set out:
- X-ray of the spine;
- MRI, CT and ultrasound of the abdominal cavity (if necessary);
- Blood and urine tests;
- Myelography;
- ECG (to rule out heart disease).
After diagnosis, a treatment regimen will be developed. There is no single regimen for the treatment of osteonecrosis: health procedures depend on the patient's condition, age, physical condition and the state of the immune system.
The main goal of treatment is to minimize the consequences of degenerative processes in the cartilage tissue and prevent the development of complications. Therapy is usually outpatient, except in particularly serious clinical situations. Mostly conservative therapy is practiced.
Medicines
The drug is prescribed only for severe pain syndromes and inflammatory processes. It is better to use the drug in the form of topical ointment, less commonly prescribed pills, intramuscular or epidural injection.
Most medicines today:
- Analgesics;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Muscle relaxants and antispasmodics;
- Vitamin complex;
- Steroids.
Experienced therapists will never offer wholly drug-based therapy. When the pain and inflammation subside, the medication is stopped.
Physiotherapy, exercise therapy, massage
These methods play a leading role in the treatment of degenerative thoracic degenerative diseases. These techniques remove pain, strengthen ligaments and muscles, restore and stimulate blood circulation and metabolism.
Common methods of physiotherapy:
- Magnetic therapy;
- Electrophoresis and electrophoresis;
- Laser exposure;
- Amplipulse therapy;
- Ultrasound treatment;
- Paraffin application;
- Kinesio Ice;
- Mud therapy;
- Balancing therapy;
- Hypothermia;
- Inheritance therapy, treatment with bee venom.
The main advantage of physiotherapy is safety. The procedure can be prescribed at any age, with almost any disease simultaneously. A separate area of physical therapy is acupressure (acupuncture). This method is effective, but requires the presence of a specialist.
Physiotherapy is a mandatory stage in the treatment of thoracic tumors. The vegetative exercise strengthens the muscle apparatus, restores the normal anatomical position of the vertebral structures, reduces the pressure on nerve ends, and prevents development of bulging and disc herniation.
Complex exercises should be done regularly and over a long period of time - only in this case do they produce a noticeable therapeutic effect. Ideally, training sessions should be performed under the guidance of an instructor, as any wrong moves can cause trauma and pain.
Massage (manual action and hardware) has the same therapeutic tasks as exercise therapy: relieving pain, improving blood flow, strengthening muscles. In addition to interacting with the therapists' hands, they are practiced to use massage machines, applicators, orthopedic appliances.
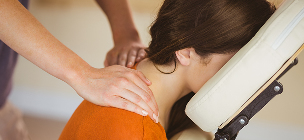
Thorough treatment
Osteoporosis in modern medical institutions is available in exceptional cases - when there is a real risk of spinal cord compression or dangerous protrusions and hernias. Spinal surgery always carries additional risks, so interventions are rarely performed and only by experienced surgeons.
Precautions
Preventing disease is much easier than long term (and sometimes lifelong) therapy. Alas, modern medicine cannot reverse degenerative processes, it can only minimize the consequences of the pathology and eliminate acute symptoms.
For this reason, the prevention of bone necrosis needs to be treated early in life. The development of the disease is hampered by: correct posture, nutritional balance, correct rotation of physical activity and rest, comfortable sleep in bed. An active role is played by timely diagnosis and serious implementation of the doctor's recommendations.

















































